Constants
Definition
C Constants is the most fundamental and essential part of the C programming language. Constants in C are the fixed values that are used in a program, and its value remains the same during the entire execution of the program.
- Constants are also called literals.
- Constants can be any of the data types.
- It is considered best practice to define constants using only upper-case names.
Constant definition in C
Syntax:
const type constant_name;
Example:
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
const int SIDE = 10;
int area;
area = SIDE*SIDE;
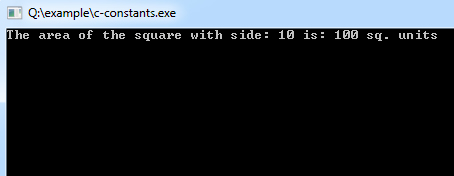
printf("The area of the square with side: %d is: %d sq. units", SIDE, area);
}
Program Output:
Constant Types in C
Constants are categorized into two basic types, and each of these types has its subtypes/categories. These are:
Primary Constants
- Numeric Constants
- Integer Constants
- Real Constants
- Character Constants
- Single Character Constants
- String Constants
- Backslash Character Constants
Integer Constant
It's referring to a sequence of digits. Integers are of three types viz:
-
Decimal Integer
-
Octal Integer
-
Hexadecimal Integer
Example:
15, -265, 0, 99818, +25, 045, 0X6
Real Constant
The numbers containing fractional parts like 99.25 are called real or floating points constant.
Single Character Constant
It simply contains a single character enclosed within ' and ' (a pair of single quote). It is to be noted that the character '8' is not the same as 8. Character constants have a specific set of integer values known as ASCII values (American Standard Code for Information Interchange).
Example:
'X', '5', ';'
String Constant
These are a sequence of characters enclosed in double quotes, and they may include letters, digits, special characters, and blank spaces. It is again to be noted that "G" and 'G' are different - because "G" represents a string as it is enclosed within a pair of double quotes whereas 'G' represents a single character.
Example:
"Hello!", "2015", "2+1"
Backslash Character Constant
C supports some character constants having a backslash in front of it. The lists of backslash characters have a specific meaning which is known to the compiler. They are also termed as "Escape Sequence".
Constants Meaning
\a beep sound
\b backspace
\f form feed
\n new line
\r carriage return
\t horizontal tab
\v vertical tab
\' single quote
\" double quote
\\ backslash
\0 null
Secondary Constants
-
Array
-
Pointer
-
Structure
-
Union
-
Enum
Array
The array is a data structure in C programming, which can store a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same data type. For example, if you want to store ten numbers, it is easier to define an array of 10 lengths, instead of defining ten variables.
In the C programming language, an array can be One-Dimensional, Two-Dimensional, and Multidimensional.
Define an array in C
Syntax:
type arrayName [ size ];
Example:
double amount[5];Initialize an array in C
int age[5]={22,25,30,32,35};
Accessing array elements
int myArray[5]; int n = 0;
// Initializing elements of array seperatelyfor(n=0;n<sizeof(myArray)/sizeof(myArray[0]);n++) { myArray[n] = n; }
int a = myArray[3]; // Assigning 3rd element of array value to integer 'a'.
Pointer
A pointer is a variable in C, and pointers value is the address of a memory location.
Pointer definition in C
Syntax:
type *variable_name;
Example:
int *width;
char *letter;
Benefits of using Pointers
- Pointers allow passing of arrays and strings to functions more efficiently.
- Pointers make it possible to return more than one value from the function.
- Pointers reduce the length and complexity of a program.
- Pointers increase the processing speed.
- Pointers save the memory.
Structure
The structure is a user-defined data type in C, which is used to store a collection of different kinds of data.
- The structure is something similar to an array; the only difference is array is used to store the same data types.
- struct keyword is used to declare the structure in C.
- Variables inside the structure are called members of the structure.
Defining a structure in C
Syntax:
struct structureName
{
//member definitions
};
Example:
struct Courses
{
char WebSite[50];
char Subject[50];
int Price;
};
Accessing structure members
Example:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
struct Courses
{
char WebSite[50];
char Subject[50];
int Price;
};
void main( )
{
struct Courses C;
//Initialization
strcpy( C.WebSite, "w3schools.in");
strcpy( C.Subject, "The C Programming Language");
C.Price = 0;
//Print
printf( "WebSite : %s\n", C.WebSite);
printf( "Book Author : %s\n", C.Subject);
printf( "Book Price : %d\n", C.Price);
}
Output:
WebSite : w3schools.in
Book Author: The C Programming Language
Book Price : 0
Unions
Unions are user-defined data type in C, which is used to store a collection of different kinds of data, just like a structure. However, with unions, you can only store information in one field at any one time.
-
Unions are like structures except it used less memory.
-
The keyword union is used to declare the structure in C.
-
Variables inside the union are called members of the union.
Defining a union
Syntax:
union unionName { //member definitions };Example:
union Courses { char WebSite[50]; char Subject[50]; int Price; };
Accessing union members
Example:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
union Courses
{
char WebSite[50];
char Subject[50];
int Price;
};
void main( )
{
union Courses C;
strcpy( C.WebSite, "w3schools.in");
printf( "WebSite : %s\n", C.WebSite);
strcpy( C.Subject, "The C Programming Language");
printf( "Book Author : %s\n", C.Subject);
C.Price = 0;
printf( "Book Price : %d\n", C.Price);
}
Output:
WebSite : w3schools.in
Book Author: The C Programming Language
Book Price : 0
Enums
In C programming, an enumeration type (also called enum) is a data type that consists of integral constants. To define enums, the enum keyword is used.
Syntax:
enum flag {const1, const2, ..., constN};
By default, const1 is 0, const2 is 1 and so on. You can change default values of enum elements during declaration (if necessary).
// Changing default values of enum constants
enum suit {
club = 0,
diamonds = 10,
hearts = 20,
spades = 3,
};