C Pointer to Pointer
As we know that, a pointer is used to store the address of a variable in C. Pointer reduces the access time of a variable. However, In C, we can also define a pointer to store the address of another pointer. Such pointer is known as a double pointer (pointer to pointer). The first pointer is used to store the address of a variable whereas the second pointer is used to store the address of the first pointer. Let's understand it by the diagram given below.

Syntax:
int **p; // pointer to a pointer which is pointing to an integer.
Example:
#include<stdio.h>
void main (){
int a = 10;
int *p;
int **pp;
p = &a; // pointer p is pointing to the address of a
pp = &p; // pointer pp is a double pointer pointing to the address of pointer p
printf("address of a: %x\n",p); // Address of a will be printed
printf("address of p: %x\n",pp); // Address of p will be printed
printf("value stored at p: %d\n",*p); // value stoted at the address contained by p i.e. 10 will be printed
printf("value stored at pp: %d\n",**pp); // value stored at the address contained by the pointer stoyred at pp
}
Output
address of a: d26a8734
address of p: d26a8738
value stored at p: 10
value stored at pp: 10
C double pointer example
Example:
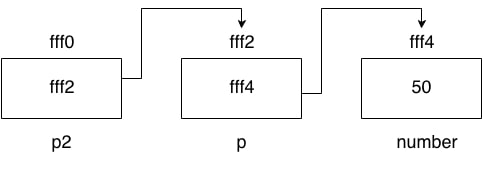
As you can see in the above figure, p2 contains the address of p (fff2), and p contains the address of number variable (fff4).
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int number=50;
int *p;//pointer to int
int **p2;//pointer to pointer
p=&number;//stores the address of number variable
p2=&p;
printf("Address of number variable is %x \n",&number);
printf("Address of p variable is %x \n",p);
printf("Value of *p variable is %d \n",*p);
printf("Address of p2 variable is %x \n",p2);
printf("Value of **p2 variable is %d \n",*p);
return 0;
}
Output
Address of number variable is fff4
Address of p variable is fff4
Value of *p variable is 50
Address of p2 variable is fff2
Value of **p variable is 50
Q. What will be the output of the following program?
#include<stdio.h>
void main (){
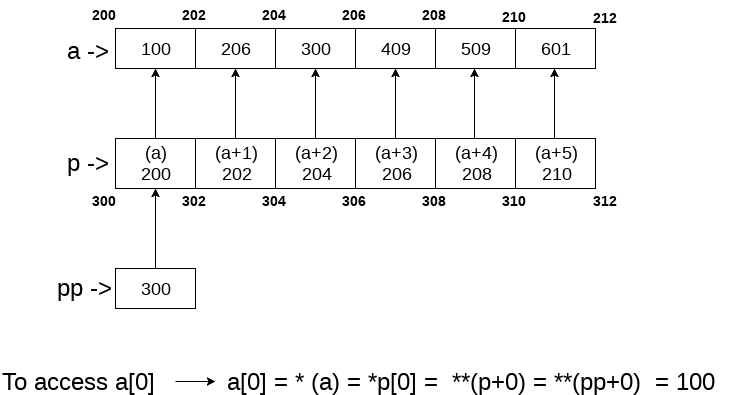
int a[10] = {100, 206, 300, 409, 509, 601}; //Line 1
int *p[] = {a, a+1, a+2, a+3, a+4, a+5}; //Line 2
int **pp = p; //Line 3
pp++; // Line 4
printf("%d %d %d\n",pp-p,*pp - a,**pp); // Line 5
*pp++; // Line 6
printf("%d %d %d\n",pp-p,*pp - a,**pp); // Line 7
++*pp; // Line 8
printf("%d %d %d\n",pp-p,*pp - a,**pp); // Line 9
++**pp; // Line 10
printf("%d %d %d\n",pp-p,*pp - a,**pp); // Line 11
}
Explanation:
Output
1 1 206
2 2 300
2 3 409
2 3 410